Addressing
Node addressing
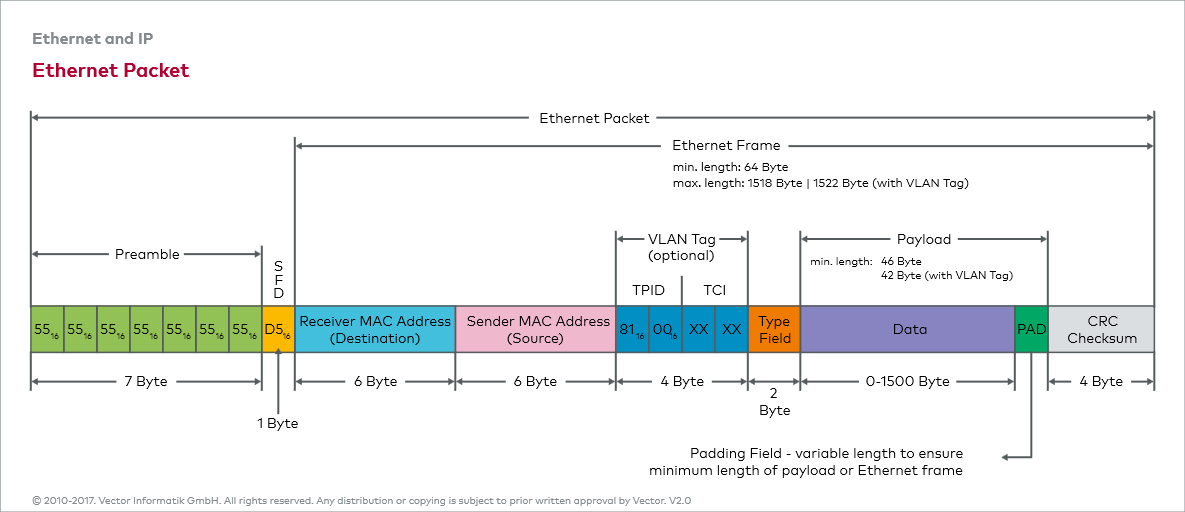
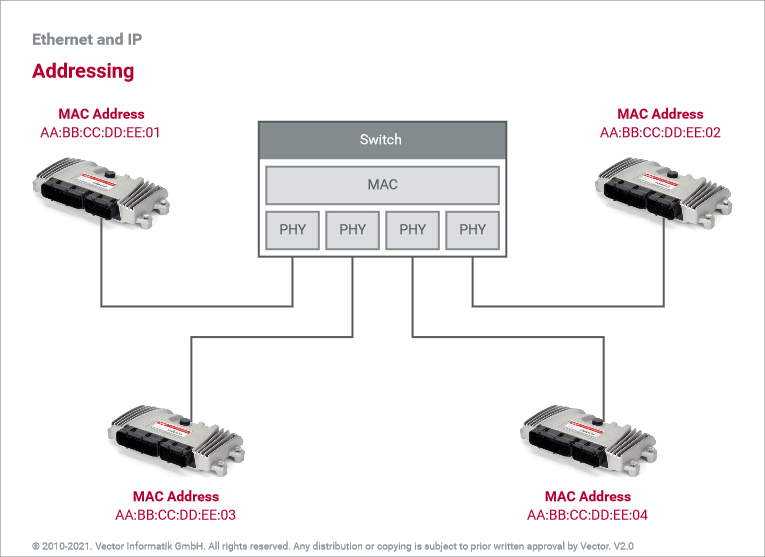
Node addressing is used for targeted delivery of messages in the Ethernet network. For this, each node has at least one MAC address that is used for unique identification in the local network (LAN). A transmitted message always contains a source and target address so that the communicating nodes can be inferred.
Unicast
The nodes are uniquely addressed using unicast addresses. The vehicle manufacturer specifies these addresses, or suppliers may select from their own address range. Address ranges can be requested from as well as registered with the IEEE Registry Authority and are uniquely assigned to a company worldwide.
Multi- and broadcast
In order for messages to be delivered to multiple nodes, multicast addresses can also be used in addition to unicast messages. These allow node groups to be defined whose members receive a message via a shared MAC address. In contrast to the broadcast address, which allows a message to be sent to all nodes, multicast addresses must be configured in the respective node.
VLAN
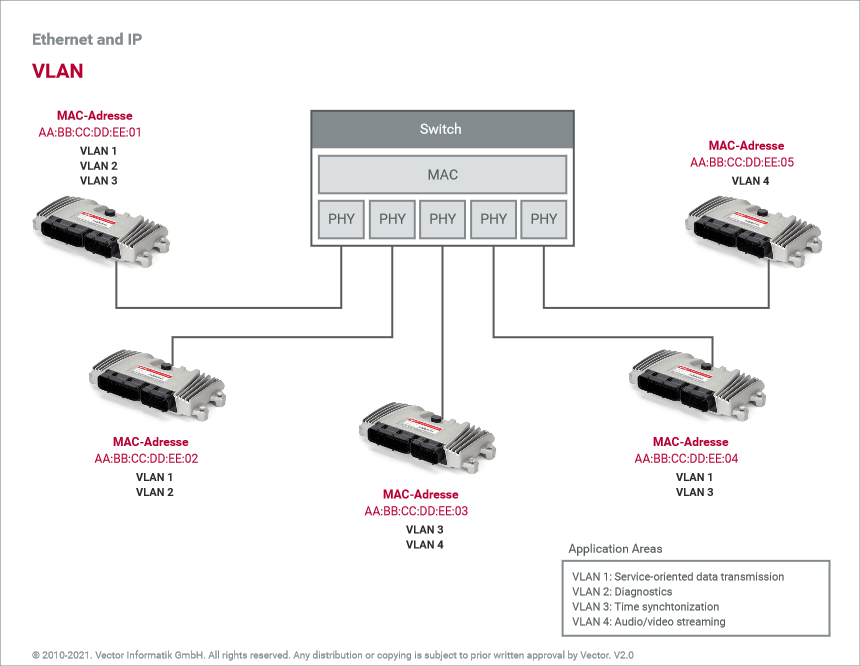
As an extension to classic addressing, VLAN addresses are frequently used in the automotive industry. These address virtual networks that are present within an overall network and allow a delimitation of communication. In this way, domains can be defined for different application areas whose members may access the communication taking place there. Because an ECU is normally active in multiple application areas, it may also be a member of multiple domains and thus multiple VLAN networks.
Priorities
To improve real-time behavior, VLAN also provides the option of defining priorities for messages. Thus, important data traffic can be routed preferentially through switches, thereby reducing latency times.