- Overview
- 1. Introduction
- 2. General Description of the Protocol
-
3. Document Structure
-
4. Fundamentals
- 4.1. Names and Addresses
- Device Names
- Device Address
- 4.2. Parameter Group
- General
- Structure and Type of a Parameter Group
- Example of a Global Parameter Group
- Example of a Specific Parameter Group
- Parameter Groups reserved specially for the Protocol
- 4.3. Data Management
- Suspect Parameter Number (SPN)
- SLOT Definition
-
5. Network Management
- Network Access
- 5.1. Address Conflict
- Solution and Configurations
- Handling in a Dynamic Network
- 6. Transport Protocols (Multi-packet Messages)
- 7. Diagnostics
Document Structure
SAE
The complete J1939 specification is subdivided into various documents and chapters. All documents can be downloaded individually or in preassembled packages from the SAE website
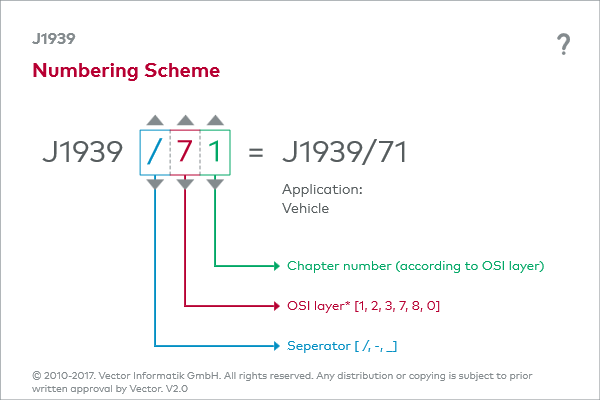
There is a charge for the individual chapters of the J1939 specification, i.e., they cannot be accessed for free. The individual chapters are structured systematically and are loosely based on the ISO/OSI reference model, which you might be familiar with from the previous chapter. Loosely based only, because the document structure of J1939 contains a chapter 8, which is not defined in the OSI model. The organization scheme of the chapters is presented in the “Numbering scheme” graphic.
Outlining
Besides the structured documents and their appendices, there is a document without number extensions. This is the J1939 top-level document in which all important features of the protocol are briefly summarized. The appendices of this document are of great importance. All parameter groups, signals, reserved node addresses, manufacturer codes, and industry groups are listed here as a quick overview.
The table on the right lists the currently existing chapters and documents.