- Overview
- 1. Introduction
- 2. General Description of the Protocol
- 3. Document Structure
-
4. Fundamentals
- 4.1. Names and Addresses
- Device Names
- Device Address
- 4.2. Parameter Group
- General
- Structure and Type of a Parameter Group
- Example of a Global Parameter Group
- Example of a Specific Parameter Group
- Parameter Groups reserved specially for the Protocol
- 4.3. Data Management
- Suspect Parameter Number (SPN)
- SLOT Definition
-
5. Network Management
- 5.1. Address Conflict
- Solution and Configurations
- Handling in a Dynamic Network
- 6. Transport Protocols (Multi-packet Messages)
- 7. Diagnostics
Network Access
Network Admission
The term network management in the J1939 context must not be confused with the network management in the usual automotive environment. The network management in the automotive environment is used to place the ECUs of a network or subnetwork in a defined and “agreed” idle state while not losing any information from the bus.
J1939 defines the term as an access control for communication (admission to the network) and administration of device addresses in dynamic networks. The device address and the NAME play an essential role in this (see chapter Names and Addresses).
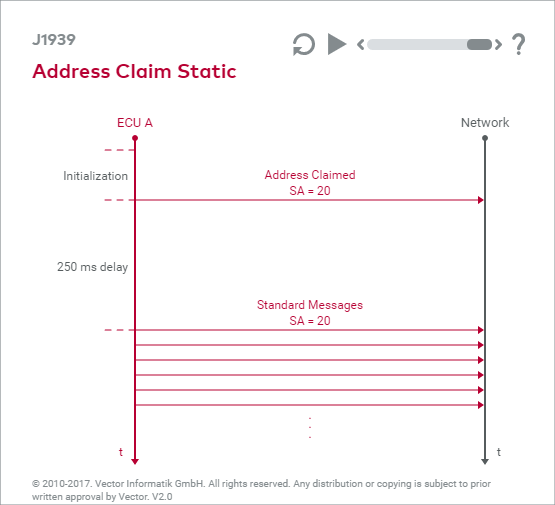
Address Claiming
The simplest form of J1939 network management is the sending out of ‘Address Claimed’ of every ECU after booting and before the actual communication begins. With “Address Claim”, the device name and a predefined device address are disclosed with the help of the ‘Address Claimed’ parameter group (PGN 0x00EE00). In static networks, this action is used mainly for disclosure of the network topology. Thus, for example, the presence of a retarder in the vehicle can be determined quickly with a diagnostic tool.
Address Conflict
“Address Claim” is also used in dynamic networks. Moreover, the network management is also used here for resolving any address conflicts that occur. These happen, for example, when an ECU is subsequently connected to a network (when operation is already underway) and this ECU uses a predefined address that is already being used in the network. This conflict must be resolved because communication requires that all addresses in the network be unique and never duplicated.