- Overview
- 1. Introduction
- 2. General Description of the Protocol
- 3. Document Structure
-
4. Fundamentals
- 4.1. Names and Addresses
- Device Names
- Device Address
- 4.2. Parameter Group
- General
- Structure and Type of a Parameter Group
- Example of a Global Parameter Group
- Example of a Specific Parameter Group
- Parameter Groups reserved specially for the Protocol
- 4.3. Data Management
- SLOT Definition
-
5. Network Management
- Network Access
- 5.1. Address Conflict
- Solution and Configurations
- Handling in a Dynamic Network
- 6. Transport Protocols (Multi-packet Messages)
- 7. Diagnostics
Suspect Parameter Number (SPN)
Data Content
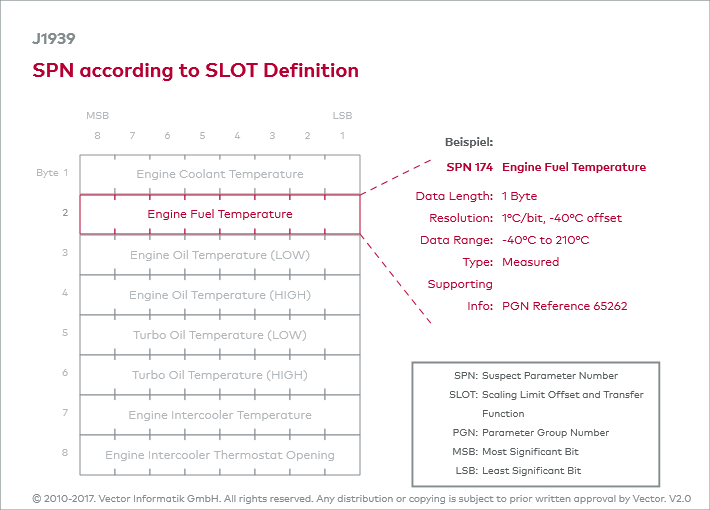
J1939 defines not only the PGNs but also their contents. Message contents are often called signals in proprietary languages. The J1939 specification has defined the following term for the PGN contents: Suspect Parameter Number (SPN). An SPN is for all intents and purposes a signal ID. It can be a physical value, a status, or a command. SPNs are also defined for internal protocol information. All specified SPNs are also currently listed in table form in J1939-DA. An SPN is a number specified by the SAE. The start position of the SPN within a PGN is specified in the PGN description (see chapter Example of a Global Parameter Group). The SPN itself is always interpreted from LSB (right) to MSB (left), except for alphanumeric data. It is possible that an SPN is present in multiple PGNs.
Every SPN is described in the definition in the same manner and has the following attributes:
General description and function of the SPN
| SPN | Suspect Parameter Number and Name |
| Description | General description of the function of an SPN |
| Data Length | Data length in bits or bytes |
| Resolution | Resolution, or conversion of the raw value to the physical value |
| Data Range | Physical, valid value range |
| Type | Type of signal, e.g., measured, status, or application-dependent signal |
| Supporting Information | <optional> |
| PGN Reference | Reference to the PGN(s) in which the SPN occurs |
The J1939 standard designates this presented SPN description as the SLOT definition (Scaling, Limit, Offset and Transfer Function).