OEM Dependencies in the Basic Software
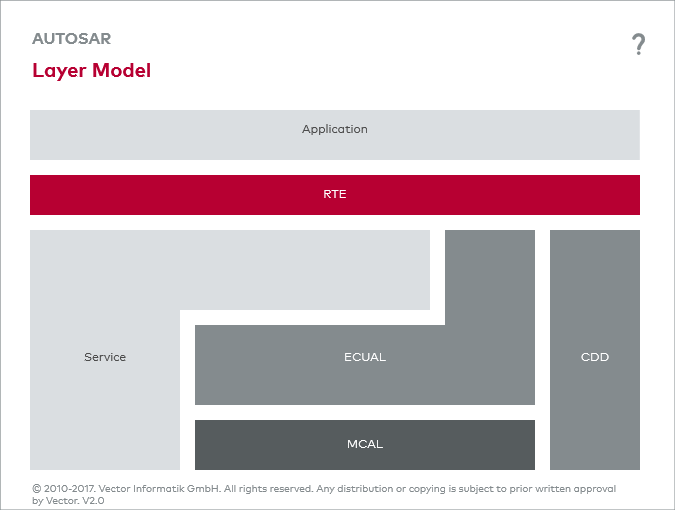
One property of AUTOSAR basic software is its high degree of modularization. This modularization is performed horizontally into different task areas (clusters) and vertically into different abstraction levels (layers). AUTOSAR permits different granularity of the Basic Software (Implementation Conformance Classes, ICC). This allows combining (clustering) BSW modules up to the monolithic basic software consisting of just one module with a functionality covering the entire basic software.
AUTOSAR Basic Software is not necessarily OEM-specific, but there are some aspects in which the BSW stacks of various OEMs typically differ.
For example, the stacks can differ in the number and task areas of specific BSW modules that are not part of the AUTOSAR standard. There could also be functional extensions to the AUTOSAR Basic Software in the form of Software Components that are added to the stack.
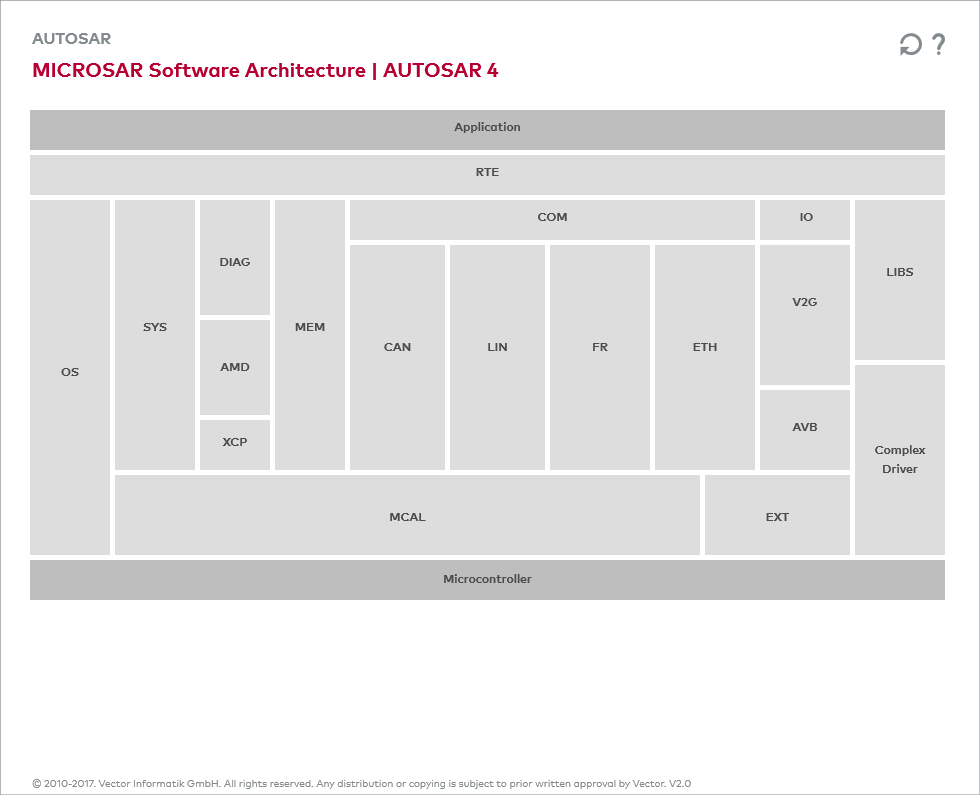
In the structure of the Basic Software, such variations occur in the following areas:
- DIAG: Diagnostic Event Manager, Diagnostic Communication Manager
- SYS: Communication Channel Handling
- COM: Network Management
- COM: Gateway functionality
- Specific services such as encryption modules, proprietary transport protocols, etc.
In terms of the configuration of the Basic Software, there are also differences in work processes at different OEMs:
- The way in which OEM requirements are supplied (.dbc file, ECU Extract of System Description or separate SWC descriptions)
- Diagnostics layout and parameter setting (ODX, CANdela file, etc.)
- General requirements such as post-build configuration capability of the communication stack, library deliveries to suppliers
The Vector implementation of the AUTOSAR standard – MICROSAR – is illustrated in the graphics on the software architecture on the right.